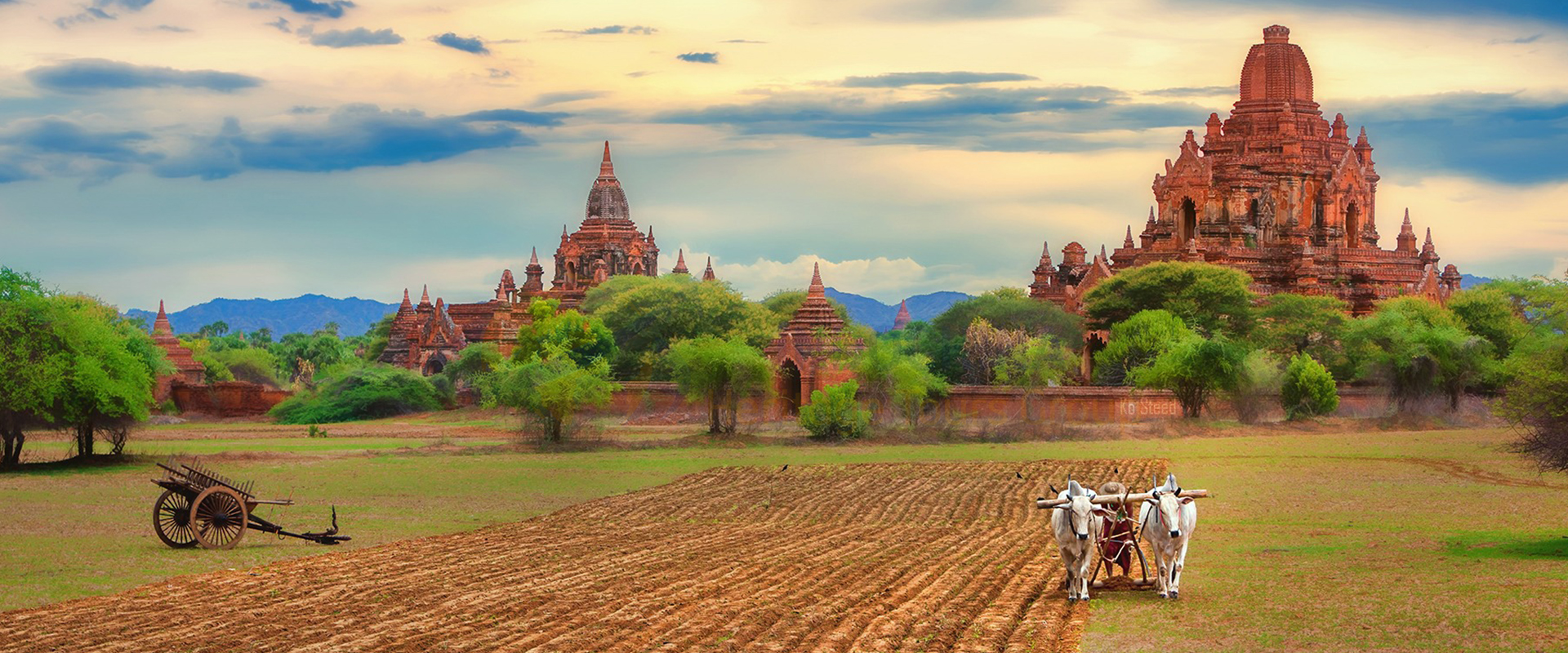
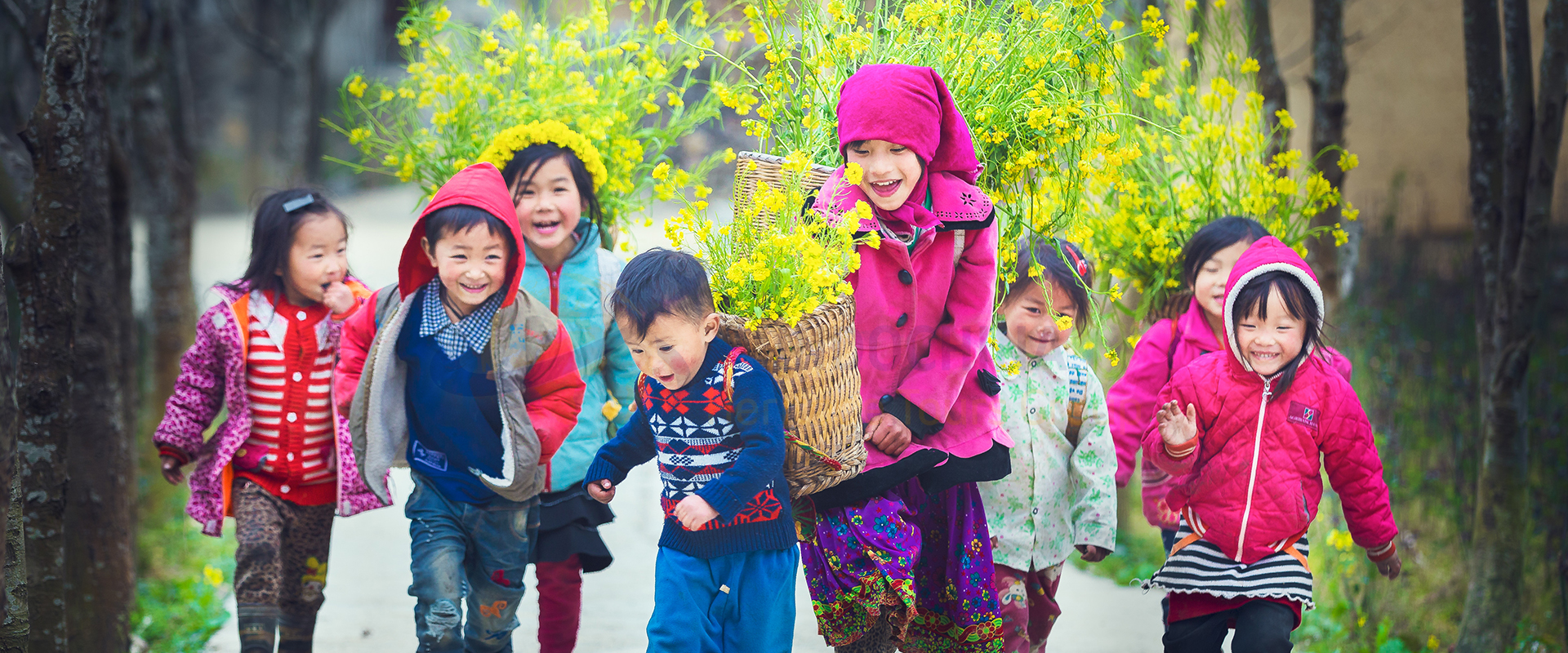
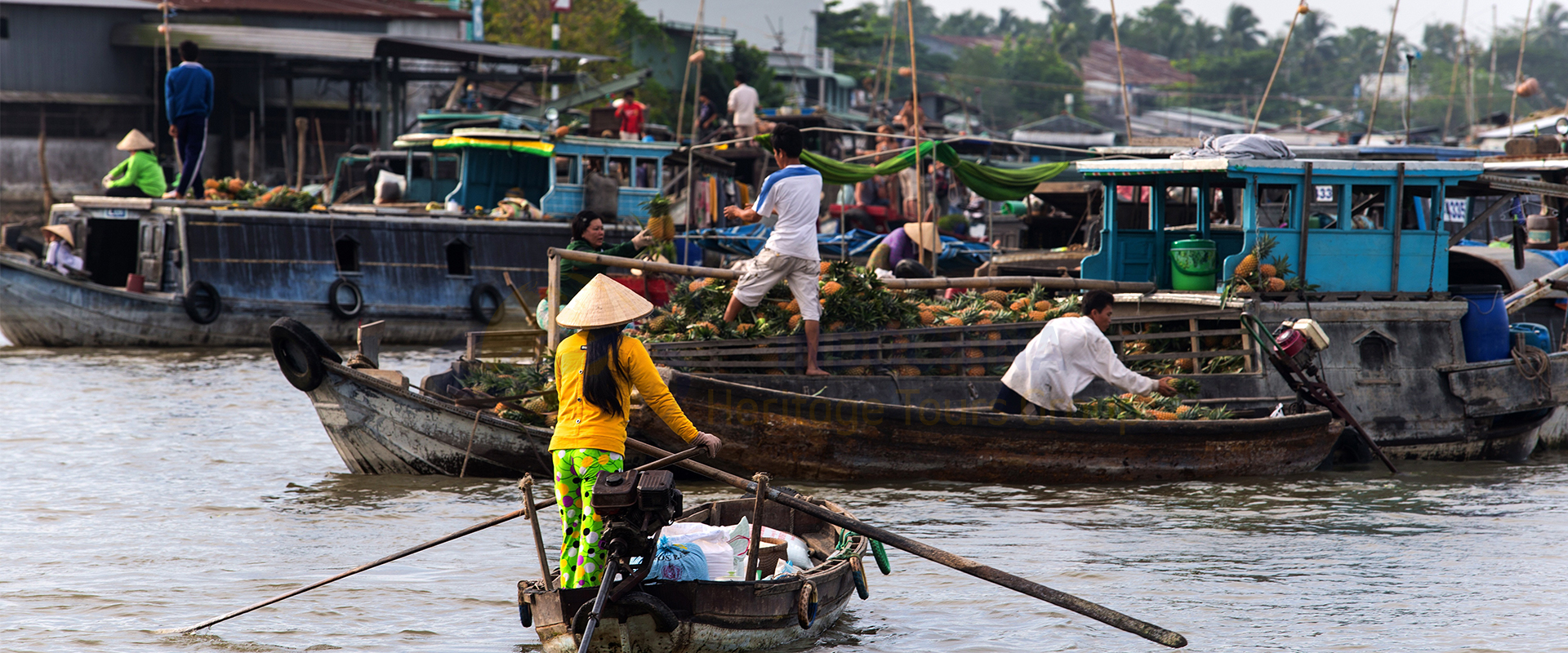
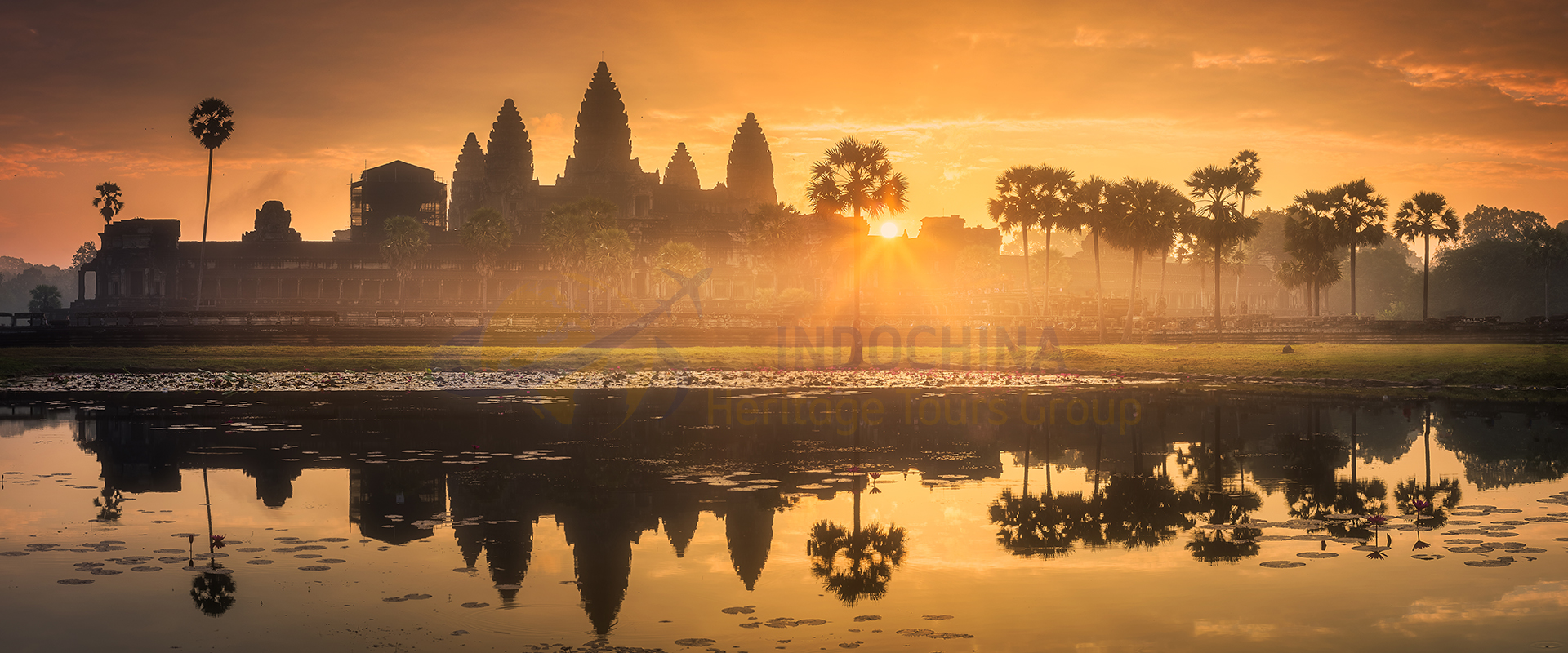
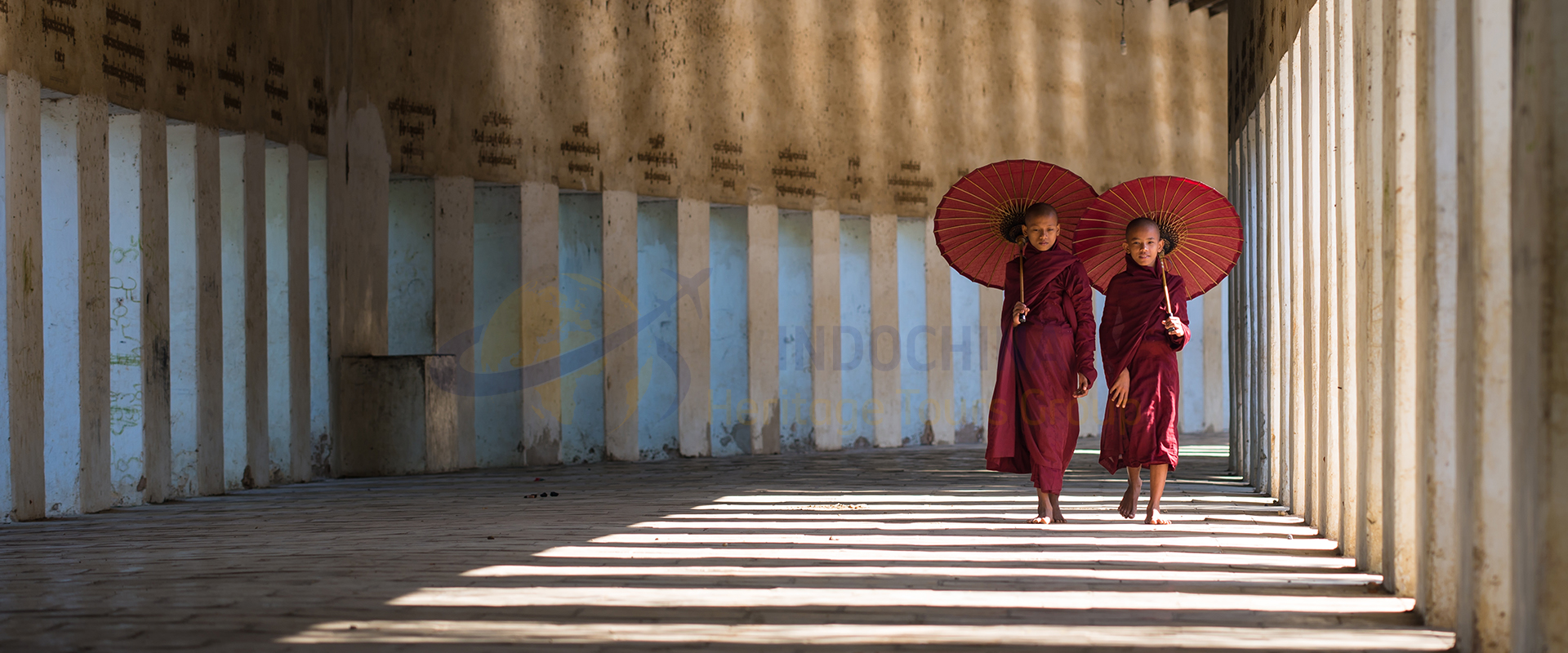
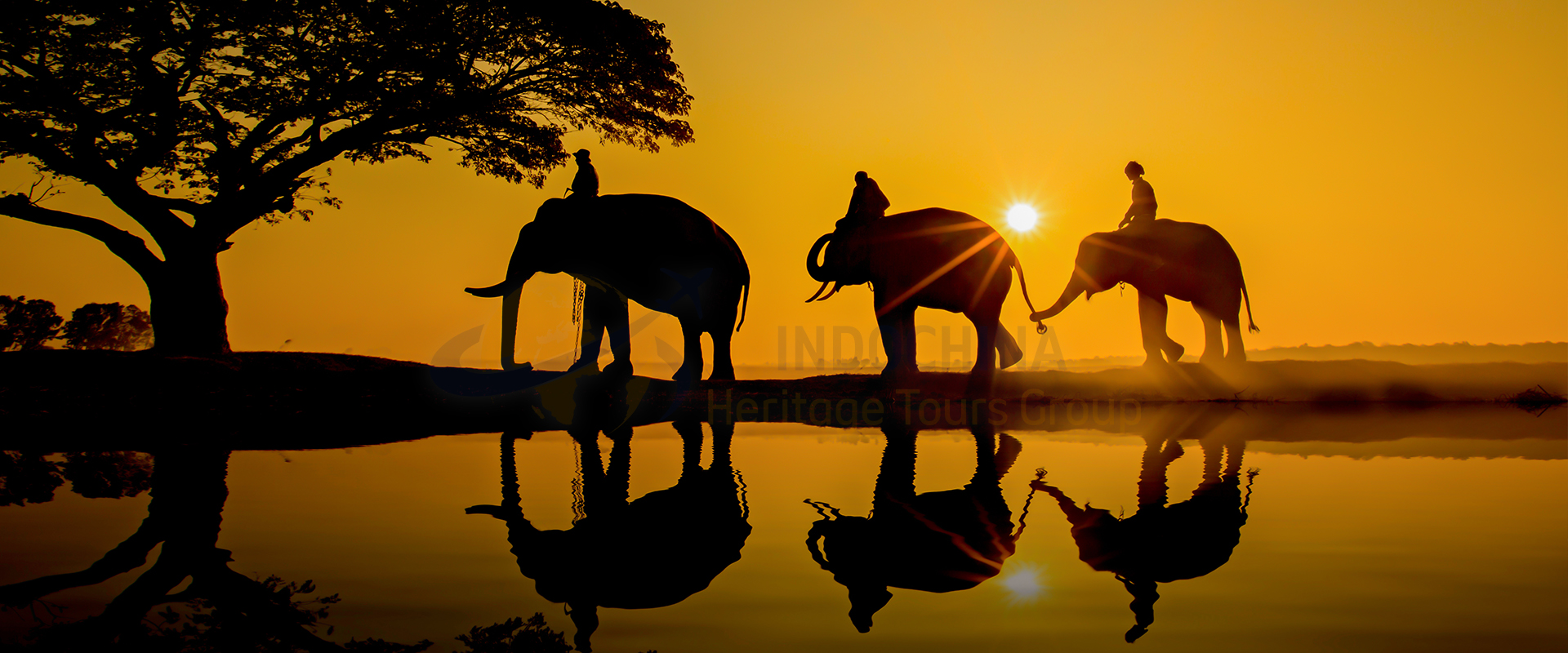
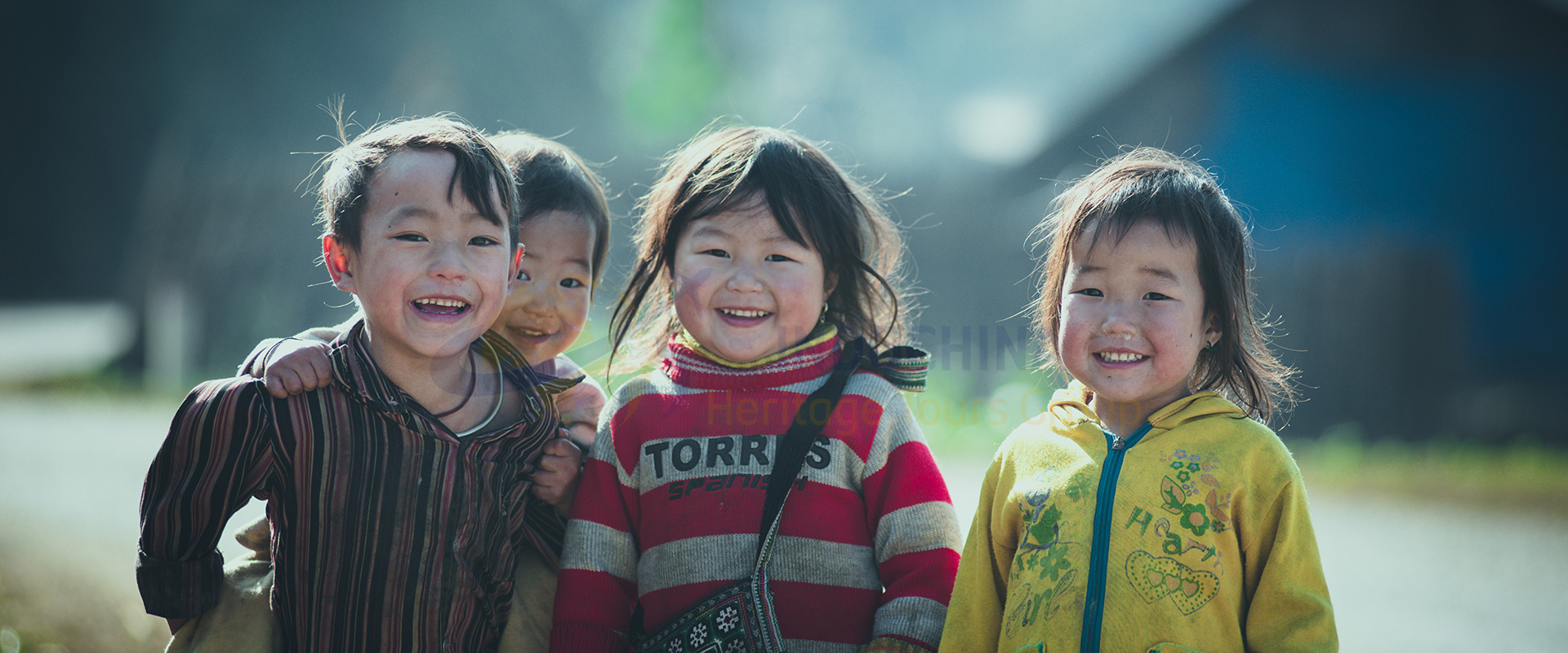
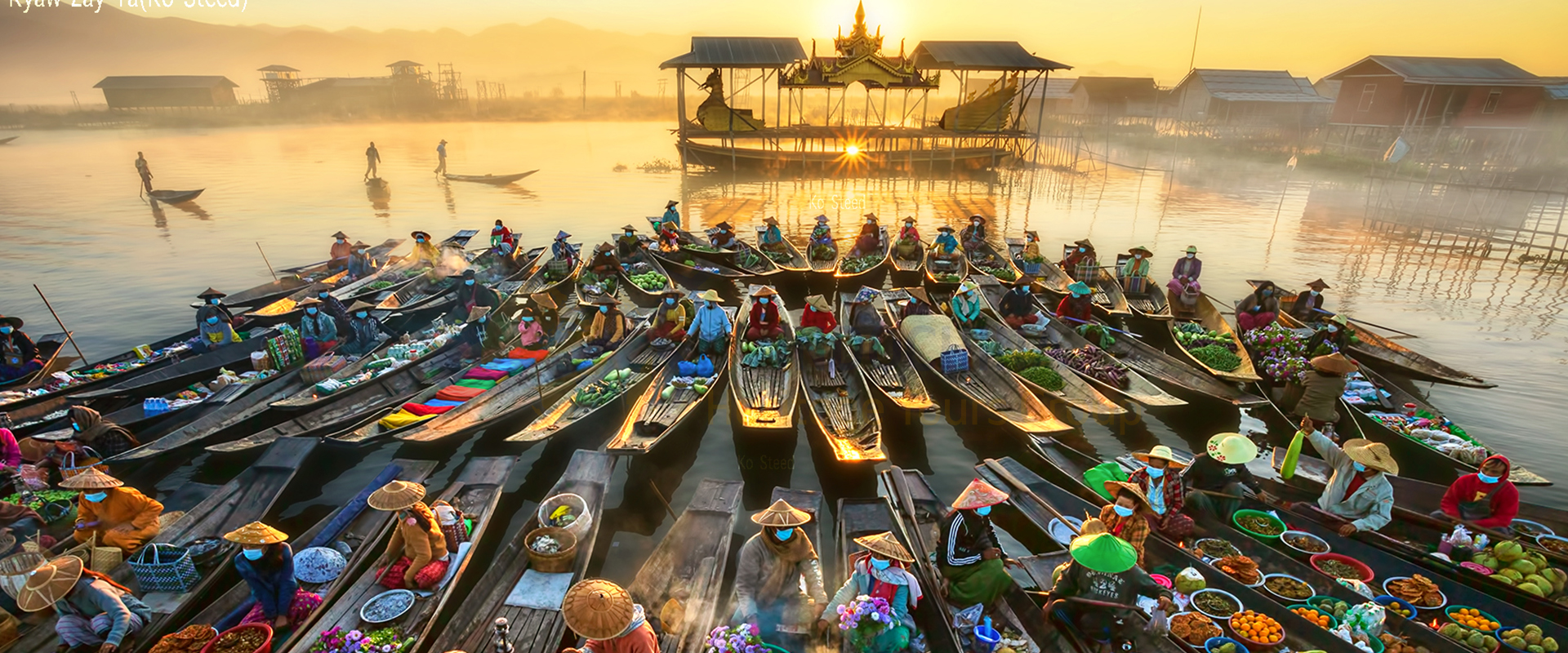
Indochina is a peninsula in Southeast Asia that borders China, India, and the South China Sea. It comprises the modern countries of Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia.
French colonization: Indochina was colonized by France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, forming the French Indochina federation. France exploited the natural resources and imposed its culture and language on the local people.
World War II and Japanese occupation: During World War II, Japan invaded and occupied Indochina, but allowed France to retain nominal control. Japan also supported nationalist movements in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia, hoping to use them as allies against the Allies.
First Indochina War: After Japan’s surrender in 1945, the Viet Minh, a communist-led nationalist movement in Vietnam, declared independence from France and fought a guerrilla war against the French and their allies. The war ended in 1954 with the Geneva Accords, which divided Vietnam into North and South, and granted independence to Laos and Cambodia.
Second Indochina War: The division of Vietnam led to a civil war between the communist North and the anti-communist South. The war also involved Laos and Cambodia, where communist rebels fought against pro-Western governments. The war ended in 1975, and the establishment of the Khmer Rouge regime in Cambodia, which committed genocide against millions of people.
Post-war era: After the war, Indochina faced economic and social challenges, such as poverty, isolation, and human rights violations. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the countries of Indochina began to adopt market reforms and open up to the world, improving their living standards and international relations. Today, Indochina is a region of cultural diversity, historical legacy, and dynamic development.